Understanding the advantages of utilizing high efficiency power supplies
By PULS Power USA
Electronics Power Supply / Management Editor Pick energy management power PULS supplies thermalEfficiency is one of the most important features that every control systems engineer/designer must consider when selecting the appropriate power supply for their application requirements. When you use a power supply, energy flows through the product, but not 100% of that energy can be used. The difference between the usable energy and what is lost is dissipated in the form of heat. Heat is the number one enemy in an electrical panel because it degrades the power supply and other surrounding electrical devices.
Let’s compare two power supplies; one is 92% efficient and the other is 96%. The 92% efficient unit is very good, so what is the point of going to 96%? Using these figures, one might think that the difference is only 4% (96%-92%=4%). Using a 100 watt power supply as an example, the 92% efficient power supply loses 8.7 watts, and the 96% efficient power supply loses 4.2 watts. That is greater than 100% less heat loss from the 96% highly efficient power supply.
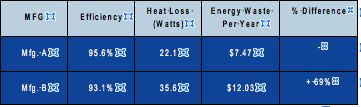
Let’s look at a real-world example using two 480 watt power supplies. Manufacturer A has an efficiency rating of 95.6%, and Manufacturer B has an efficiency rating of 93.1%. The apparent difference is 2.5%. Not a big deal, right? The table below demonstrates the actual differences between these two power supply units.
Based on 50 hours of operation per week and $0.13 per KW.
Considerations of Heat
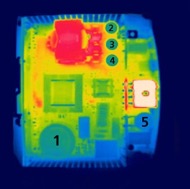
Heat is the number one enemy to a power supply because electrolytic capacitors are used in all switch mode power supply designs and electrolytic capacitors degrade at a higher rate in high ambient temperature applications. Often times, there are far more sensitive electronic components inside an enclosure which can be affected by heat like PLC’s, industrial computers, communication devices, and HMIs. Heat can radically change the reliability and lifetime of the power supply and in many cases can force you to increase your enclosure size, install some form of cooling and/or derate the unit to compensate for high heat losses. The general rule of thumb as published by capacitor manufacturers is that every 10°C increase in temperature results in a 50% decrease in life of the capacitor/power supply. Since capacitors are very sensitive to heat, a good power supply design will also thermally separate the capacitors from heat producing components like transformers and bridge rectifiers. As shown in the thermal image below, the larger blue circle (1) at the bottom, and the 3 smaller blue circles (2, 3, 4) in the upper right are electrolytic capacitors. These capacitors are positioned so that they are either placed in a naturally cooler location (bottom), or they are separated by an air channel that protects them from stagnant heat and therefore extends their lifetime and reliability. More importantly, reduced heat will lengthen the life of all products, substantially reduce replacement costs, and provide a lower total cost of ownership.
So, by choosing a power supply with the highest efficiency and good thermal design can mean the difference between a highly reliable control system and a system where problems ultimately will occur.
Energy Savings
Another area that should be carefully considered by the designer is the amount of lost energy consumption required to operate the load. If we look back at the same example of the two 480 watt power supplies, but this time from an energy standpoint, you will be surprised with the results. The power supply which was rated 93.1% efficient from Manufacturer B had 35.6W of lost energy and from a simplistic calculation loses 1.78KW over a 50-hour work week. As compared to the 95.6% efficient power supply from Manufacturer A, with losses of only 1.1kW over the same period. Using an average kilowatt cost of $0.13 per kilowatt/hour, the lower efficient power supply from Manufacturer B would waste approximately $12.03 per year versus $7.47 per year for Manufacturer A, Multiply this by the number of power supplies utilized in a facility and the savings can be quite significant over the life of the control system.
Total Cost of Ownership
Let’s look at examples of 3 different brands of 240 watt Power Supplies. If we calculate energy losses, and lifetime over a 10-year period for a facility with 50 power supplies and a 40°C ambient temperature, we can see the true difference in costs. Manufacturer A has 14.5W of losses and a lifetime of 57,000 hours based on the data from the manufacturer of the electrolytic capacitors that were used in that power supply. Manufacturer B has 18.8W of losses and a lifetime of 18,000 hours, and Manufacturer C has 17.6W of losses and a lifetime of 34,000 hours. The table below shows the true cost of ownership of each power supply brand.
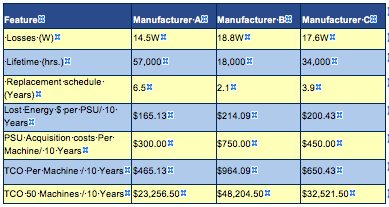
Based on 24/7 operation and $0.13 per KW.
The Bottom Line
This data shows the many significant impacts of choosing the right manufacturer for an efficient power supply. Key benefits to the customer are:
- Lower Energy costs over the lifetime of the application
- Reduced Heat introduced into the control enclosure, potentially eliminating the need for cooling systems or oversizing the enclosure
- Reduced Stress on the electrolytic capacitors and other electronics increasing the lifetime of all devices in the enclosure
- Fewer replacements over the life of the application
- Lower total cost of ownership for the system
Best practices when determining which brand to choose include the insistence of the highest full and partial load efficiencies, documented lifetime of the electrolytic capacitors, (not just calculated MTBF) accurate and detailed data sheets and of course, the lowest total cost of ownership.
————————————————————–
PULS is a manufacturer of DIN-Rail and machine mount switch mode power supplies and dc power products.