Wearable patch gives diabetics painless glucose monitoring
By University of Waterloo Media Relations
Electronics Engineering Medical Wearable Technology medical patch university Waterloo wearableUniversity of Waterloo researchers developing an alternative to traditional tests
University of Waterloo researchers are developing a new patch that would offer diabetics an affordable, accurate, pain-free, round-the-clock alternative to traditional tests that require pricking a finger for a blood sample every few hours. And, to make it even more user-friendly, potentially life-saving readings from the patch would be transmitted to people’s smartphones.
After three years of work, the research team is perfecting a wearable patch that uses hundreds of tiny microneedles to sense glucose levels, crucial information for diabetics who need to know exactly how much medication they require at any one time.
Make it easier for people to monitor
“This will improve people’s lifestyle by leading to more personalized medicine-taking,” said Peyman GhavamiNejad, an engineering PhD student at Waterloo who led the work. “We want to make it easier for people to monitor themselves, without any pain, with better control of the levels of their glucose and so they know how much insulin to take.”
Although a variety of monitoring patches have been commercially available for several years, GhavamiNejad said this is the first of its kind.
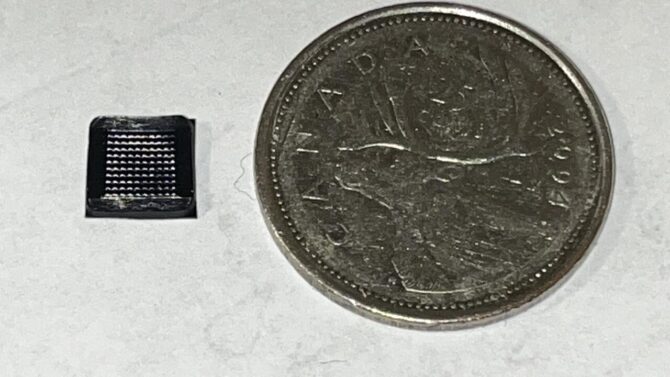
This photo illustrates the size of the sensor, positioned next to a Canadian ‘quarter’ or 25-cent piece. Source: University of Waterloo
“It’s really novel work that we continue to improve,” he said of the electro-chemical sensor. “Before this no one’s done it with hydrogel conductive material that could be used for glucose sensing as a microneedle platform.”
There are distinct advantages to the new patch, according to Dr. Mahla Poudineh, an electrical and computer engineering professor who leads the overall project. For example, patients can apply the patch themselves, unlike some other devices that must be inserted under the skin by a nurse.
Miniature electronic platform to wirelessly send readings
The patch would be extremely small — only a centimetre square — so it could be worn very discreetly on a person’s arm. Because it uses low-cost materials, it would be cheaper than some of the patches now available, which can cost up to $4,800 a year, and it could be purchased by patients over the counter. It would also give more accurate and continual measurements for 14 days, compared to current devices that provide monitoring for seven to 10 days.
In conjunction with the work being done by GhavamiNejad, Poudineh and the rest of their team, Dr. Peter Levine, an electrical and computer engineering professor, is building a miniature electronic platform to wirelessly send readings from the microneedles to users’ smartphones.
The project is funded by a Discovery Grant from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.